Over the past decades, majority of the research on microwave imaging have been conducted for breast cancer detections. Recently, this technique has been applied to other parts of the human body for stroke and congestive heart failure detection due to the difference between the dielectric constants of healthy and unhealthy tissues. Ultra-wideband (UWB) radar based imaging works by transmitting a short pulse towards a target and its scattered field is measured. On the other hand, wearable devices have been gaining widespread attention from various fields namely medical and consumer market. The idea of Internet of Thing (IoT), where every device is connected to each other has also opened up many possibilities especially for real-time health monitoring of patients.
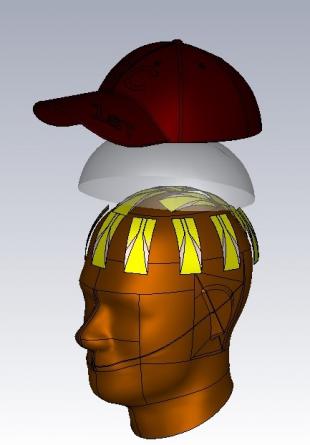
In this research, we propose a wearable radar-based UWB medical microwave imaging technology to realise an almost-real-time detection of brain diseases such as cancer and stroke where microwave tomography methods are severely hindered due to their very high computational requirements. The proposed wearable imaging system will utilise several conformal antennas placed around the head on a cap-like structure. Compared to other research works on microwave head imaging, this system will have significant advantages like constant monitoring of the patient's health as well as removal of the need for mechanical rotational platform to rotate the antenna around the head.
The key objectives of the research include:
- To investigate the interaction between electromagnetic waves and biological tissue
- To miniaturise ultra-wideband antenna for wearable applications
- To fabricate artificial human body for testing using low cost and harmless materials
- To explore flexible subsrates suitable for wearable devices